In this article, we will see how to install flatpak on Ubuntu 22.04. Flatpak is a free and open source utility for software deployment, application virtualization, and package management that aims to provide a universal packaging format for applications on Linux systems. It allows developers to distribute their applications in a way that is independent of the distribution and version of the operating system. It is also quite easy to install and use in almost all the famous linux platforms. Here we will see the steps to install flatpak on Ubuntu 22.04 based systems.
Key Features
- Sandboxing: Flatpak uses a sandboxing mechanism to isolate applications from each other and from the host system. This increases security by limiting the potential impact of vulnerabilities in applications and provides a controlled environment for running applications.
- Cross-Distribution Compatibility: Flatpak allows applications to be packaged once and run on any Linux distribution that supports Flatpak, eliminating the need for developers to create different packages for different distributions.
- Bundled Dependencies: Applications packaged as Flatpaks contain most of their dependencies, reducing compatibility issues and ensuring that the application runs in a consistent environment, regardless of the host system's configuration.
- Easy Installation and Updates: Flatpak provides a streamlined process for installing and updating applications. Users can easily install Flatpak applications from various repositories, with Flathub being the most popular one.
- Rollback and Branching: Flatpak supports versioning, allowing users to rollback updates if needed and developers to maintain multiple branches of their applications, such as stable and nightly builds.
- Command-Line and Graphical Interfaces: While Flatpak can be used through the command line, it is also integrated into various graphical software centers, making it accessible to users who prefer graphical interfaces.
Components
- Runtimes: These are the base libraries and utilities that applications need to run. Runtimes are shared among applications, reducing redundancy and saving disk space.
- Applications: These are packaged with the specific dependencies they need that are not included in the runtime. Each application is sandboxed and isolated from the system and other applications.
- Repositories: Locations from which Flatpak applications and runtimes can be downloaded. Flathub is the most well-known Flatpak repository, hosting a wide range of applications.
How It Works
When a developer packages an application as a Flatpak, they specify which runtime the application requires. The application is then bundled with any additional dependencies it needs that are not provided by the runtime. Users can install the runtime and the application from a Flatpak repository. When the application is run, it uses the runtime and its own bundled dependencies, isolated from the rest of the system by the sandbox.

How to Install flatpak on Ubuntu 22.04
Also Read: How to Install Trivy Vulnerability Scanner on Ubuntu or Debian
Step 1: Prerequisites
a) You should have a running Ubuntu 22.04 Server.
b) You should have sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
c) You should have apt or apt-get utility available in your Server.
d) Minimum hardware requirements for installation:-
- Processor: 2 GHz dual-core processor
- RAM: 4 GB
- Hard Drive: 25 GB of free space (more if you plan to install many applications)
- Graphics Card and Monitor: Capable of 1024 x 768 resolution (though higher is recommended for a better experience)
Step 2: Update Your Server
To ensure that your system's package index is up-to-date and all installed packages are upgraded to their most recent versions, run sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Step 3: Install flatpak
You can install flatpak from default Ubuntu repo by using sudo apt install flatpak command as shown below. This will download and install the package along with all its required dependencies.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install flatpak Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libappstream-glib8 libfuse2 libmalcontent-0-0 libostree-1-1 Suggested packages: malcontent-gui The following NEW packages will be installed: flatpak libappstream-glib8 libfuse2 libmalcontent-0-0 libostree-1-1 0 upgraded, 5 newly installed, 0 to remove and 11 not upgraded. Need to get 1,918 kB of archives. After this operation, 6,700 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libappstream-glib8 amd64 0.7.18-2ubuntu1 [156 kB] Get:2 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libfuse2 amd64 2.9.9-5ubuntu3 [90.3 kB] Get:3 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libmalcontent-0-0 amd64 0.10.4-1 [22.7 kB] Get:4 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libostree-1-1 amd64 2022.2-3 [333 kB] Get:5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 flatpak amd64 1.12.7-1 [1,316 kB] Fetched 1,918 kB in 2s (796 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libappstream-glib8:amd64. (Reading database ... 243839 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libappstream-glib8_0.7.18-2ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libappstream-glib8:amd64 (0.7.18-2ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libfuse2:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libfuse2_2.9.9-5ubuntu3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libfuse2:amd64 (2.9.9-5ubuntu3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libmalcontent-0-0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libmalcontent-0-0_0.10.4-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libmalcontent-0-0:amd64 (0.10.4-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libostree-1-1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libostree-1-1_2022.2-3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libostree-1-1:amd64 (2022.2-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package flatpak. Preparing to unpack .../flatpak_1.12.7-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking flatpak (1.12.7-1) ... Setting up libappstream-glib8:amd64 (0.7.18-2ubuntu1) ... Setting up libostree-1-1:amd64 (2022.2-3) ... Setting up libfuse2:amd64 (2.9.9-5ubuntu3) ... Setting up libmalcontent-0-0:amd64 (0.10.4-1) ... Setting up flatpak (1.12.7-1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for dbus (1.12.20-2ubuntu4.1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.6) ...
Step 4: Verify Installation
To display the status of flatpak installation, run dpkg -s flatpak command as shown below. Below command outputs various information about the flatpak package, such as its version, description, installation status, and architecture. Check 21+ Practical dpkg Command Examples for Linux Beginners to know more about dpkg command usage.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ dpkg -s flatpak Package: flatpak Status: install ok installed Priority: optional Section: admin Installed-Size: 4821 Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <[email protected]> Architecture: amd64 Version: 1.12.7-1 Replaces: xdg-app Depends: adduser, bubblewrap (>= 0.4.0), default-dbus-system-bus | dbus-system-bus, xdg-dbus-proxy (>= 0.1.0), libappstream-glib8 (>= 0.6.1), libarchive13 (>= 3.0.4), libc6 (>= 2.34), libdconf1 (>= 0.26.0), libfuse2 (>= 2.9.2), libgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0), libglib2.0-0 (>= 2.67.3), libjson-glib-1.0-0 (>= 1.5.2), libmalcontent-0-0 (>= 0.6.0), libostree-1-1 (>= 2020.8), libpolkit-agent-1-0 (>= 0.105), libpolkit-gobject-1-0 (>= 0.101), libseccomp2 (>= 2.5.2), libsoup2.4-1 (>= 2.41.90), libsystemd0, libxau6 (>= 1:1.0.9), libxml2 (>= 2.7.4), libzstd1 (>= 1.4.0) Recommends: ca-certificates, desktop-file-utils, hicolor-icon-theme, gtk-update-icon-cache, libpam-systemd, p11-kit, policykit-1, shared-mime-info, xdg-desktop-portal (>= 1.6), xdg-desktop-portal-gtk (>= 1.6) | xdg-desktop-portal-backend, xdg-user-dirs Suggests: avahi-daemon, malcontent-gui ........................................
Step 5: Check version
You can check the current installed version by running flatpak --version command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ flatpak --version Flatpak 1.12.7
Step 6: Using flatpak
Once Flatpak is installed, you can add the Flathub repository with a single command:-
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
After adding the Flathub repository, you can search for and install applications using the flatpak command or through a graphical software manager that supports Flatpak, like GNOME Software or KDE Discover. For example, if you are looking to install stable Arduino IDE then you have to use sudo flatpak install flathub cc.arduino.arduinoide command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo flatpak install flathub cc.arduino.arduinoide [sudo] password for itsfosslinux: Looking for matches… Required runtime for cc.arduino.arduinoide/x86_64/stable (runtime/org.freedesktop.Platform/x86_64/23.08) found in remote flathub Do you want to install it? [Y/n]: Y cc.arduino.arduinoide permissions: ipc network x11 devices file access [1] [1] home ID Branch Op Remote Download 1. [✓] org.freedesktop.Platform.GL.default 23.08 i flathub 162.4 MB / 162.3 MB 2. [✓] org.freedesktop.Platform.GL.default 23.08-extra i flathub 17.9 MB / 162.3 MB 3. [✓] org.freedesktop.Platform.Locale 23.08 i flathub 17.9 kB / 359.9 MB 4. [✓] org.freedesktop.Platform.openh264 2.2.0 i flathub 1.2 MB / 944.3 kB 5. [✓] org.freedesktop.Platform 23.08 i flathub 185.2 MB / 225.6 MB 6. [\] cc.arduino.arduinoide stable i flathub 60.8 MB / 183.8 MB Installing 6/6… ████▏ 21% 4.3 MB/s 00:52 ......................................
Step 7: Run an application
To run an application, you can use flatpak run command. For example, in our case we are launching Arduino IDE by running flatpak run cc.arduino.arduinoide command as shown below. When you execute this command, Flatpak looks for the installed package with the ID cc.arduino.arduinoide and starts the application in a sandboxed environment. This sandboxing provides a secure, isolated context for the application, limiting its access to the host system to improve security and reproducibility.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ flatpak run cc.arduino.arduinoide
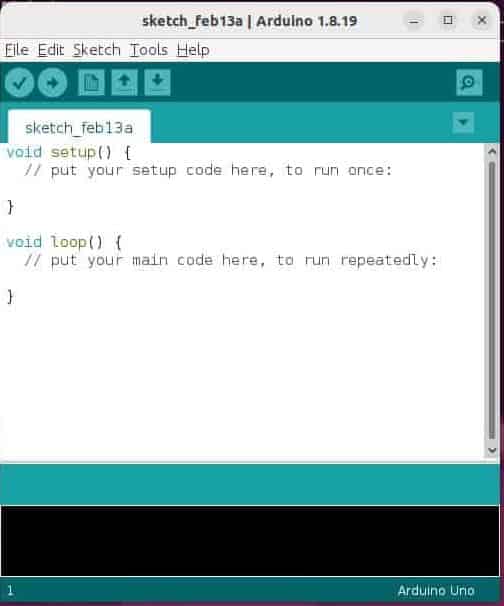
Step 8: Remove an application
You can also choose to remove an installed application by using flatpak remove command. For example, in our case we are removing Arduino IDE application by using sudo flatpak remove cc.arduino.arduinoide command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo flatpak remove cc.arduino.arduinoide ID Branch Op 1. [-] cc.arduino.arduinoide stable r Uninstalling… Note that '/var/lib/flatpak/exports/share' is not in the search path set by the XDG_DATA_HOME and XDG_DATA_DIRS environment variables, so applications may not be able to find it until you set them. The directories currently searched are: - /root/.local/share ID Branch Op 1. [-] cc.arduino.arduinoide stable r Uninstall complete.
Step 9: List all installed applications
To check all installed applications and runtimes, run flatpak list command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ flatpak list
Name Application ID Version Branch Installation
Arduino IDE cc.arduino.arduinoide 1.8.19 stable system
Freedesktop Platform org.freedesktop.Platform 23.08.11 23.08 system
Mesa org.freedesktop.Platform.GL.default 23.3.4 23.08 system
Mesa (Extra) org.freedesktop.Platform.GL.default 23.3.4 23.08-extra system
openh264 org.freedesktop.Platform.openh264 2.1.0 2.2.0 system
Step 10: Check all available options
You can also check all the command line options available with flatpak utility using flatpak --help command as shown below.
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ flatpak --help
Usage:
flatpak [OPTION…] COMMAND
Builtin Commands:
Manage installed applications and runtimes
install Install an application or runtime
update Update an installed application or runtime
uninstall Uninstall an installed application or runtime
mask Mask out updates and automatic installation
pin Pin a runtime to prevent automatic removal
list List installed apps and/or runtimes
info Show info for installed app or runtime
history Show history
config Configure flatpak
repair Repair flatpak installation
create-usb Put applications or runtimes onto removable media
..............................................
Also Read
Step 11: Uninstall flatpak
Once you are done using flatpak, you can choose to remove it from your system by using sudo apt remove flatpak command as shown below. However, this command may leave behind configuration files associated with flatpak and some package dependencies that were installed alongside it but are not removed by default to avoid breaking other packages that might depend on them. If you also want to remove these leftover configuration files and unneeded dependencies, you can use the sudo apt purge flatpak command (to remove configuration files) and sudo apt autoremove (to remove unneeded dependencies).
itsfosslinux@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt remove flatpak [sudo] password for itsfosslinux: Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: libappstream-glib8 libfuse2 libmalcontent-0-0 libostree-1-1 Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following packages will be REMOVED: flatpak 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 11 not upgraded. After this operation, 4,937 kB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y (Reading database ... 243986 files and directories currently installed.) Removing flatpak (1.12.7-1) ... Processing triggers for dbus (1.12.20-2ubuntu4.1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ...
